
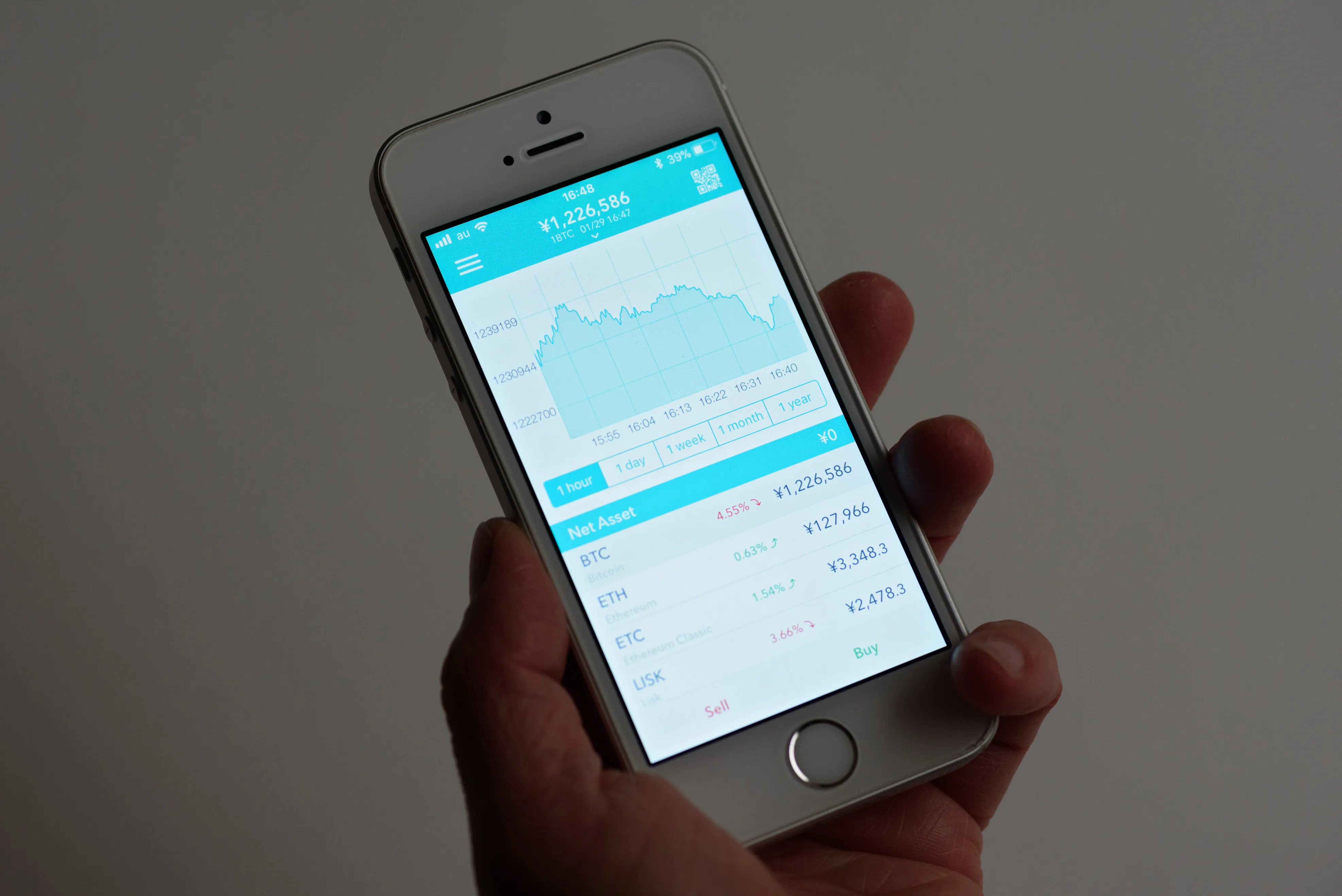
The Coincheck hack demonstrated the importance of using some basic security measures with cryptocurrencies.

These hacks have raised serious questions about the security of cryptocurrencies and blockchain around the world. Japanese exchange Coincheck first confirmed the hack on January 26, 2018, confessing that more than $500 million worth of digital coins had been stolen by hackers from the Japanese cryptocurrency exchange.
COINCHECK HACKERS CODE
The unknown attacker simply exploited Bitcoin by flooding the code to create an extremely large amount of Bitcoin.Īnother one of the biggest attacks on blockchain technology occurred in Tokyo earlier this year, with the Coincheck hack.
COINCHECK HACKERS SOFTWARE
Back in 2010, a hacker manipulated a bug in Bitcoin’s software to generate a block that contained 92 billion bitcoin, which is 91,979,000,000 more bitcoin than the intended cap on bitcoin supply. The first widely publicized hack involved Bitcoin-the most prevalent application of blockchain. In fact, blockchain technology proved long ago that it is hackable. But despite the benefits of blockchain, even the best-designed blockchain systems are not immune to attack. As a de-centralization technology where users can remain anonymous, blockchain makes it hard for regulators to deal with and allows for potential security threats. As with all technology, blockchain has its own weak points. This makes it difficult to hack a single record because the hacker would need to change the block containing that record as well as those linked to it to avoid detection. Moreover, because blockchains are decentralized and distributed across peer-to-peer networks that aren’t contained in a central location, blockchains don’t have a single point of failure and cannot be changed from a single computer.īlockchain technology has the possibility to solve data breach problems by removing the trust involved in the storage and access of digital content. Thus, no single entity can take control of the data in the blockchain. Each block is then linked to a specific participant. Blockchain can only be updated by consensus between users in the system, and when new data is entered, it can never be erased, edited, adjusted, or changed.īecause blockchain uses cryptography to connect the contents of the newly added block with each block before it, any change to the contents of a previous block in the chain would invalidate the data in all blocks following it.

Each transaction, or “block”, is time-stamped and linked to the previous one. Gox.Blockchain technology is seeing increasingly wide use internationally, but security issues are becoming a major problem.īlockchain is a public electronic ledger that can be openly shared among users and that creates an unchangeable record of their transactions. The hackers stole the NEM currency from Coincheck in late January in the largest digital currency heist in history, which eclipsed the 2014 theft of 48 billion yen in bitcoin from the now-defunct Mt. "Exchange operators need to make prior agreements on the handling of stolen virtual coins," he added. Chief Technology Officer Masanori Kusunoki, who is versed in cryptocurrency, said, "It has become evident we cannot block currency laundering just because all transactions are recorded." Some exchange operators, alerted by an increase in NEM trading, have tried to block suspicious transactions, but those possessing NEM linked to marked accounts simply take the currency elsewhere, it said. There have been cases where such marks were erased. The organization has called on virtual currency exchanges around the world not to process NEM payments from the marked accounts. The NEM Foundation, a Singapore-based organization promoting the virtual currency, has been tracking stolen NEM by marking accounts used for illicit transfers.

Transactions are still being made on the website, suggesting more of the stolen NEM could be laundered and become impossible to trace, according to the expert. The hackers set up a website on the dark web for trading virtual coins and began converting the NEM coins on Feb. The converted coins may have been exchanged to other virtual currencies or cashed by the hackers through the highly anonymous "dark web," making it even more difficult to track the stolen coins worth 58 billion yen ($547 million) at the time of the heist. into other virtual coins for laundering, a cybersecurity expert said Saturday. Hackers may have converted half of the NEM cryptocurrency stolen from Tokyo-based bourse operator Coincheck Inc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
